Us news and world top universities – US News & World Report Top Universities, a prestigious global ranking system, unveils a captivating world of academic excellence, research prowess, and student success. This comprehensive analysis delves into the methodology behind these rankings, exploring the intricate factors that contribute to a university’s standing on the global stage.
From renowned institutions in the United States to leading universities across continents, the rankings provide a valuable snapshot of the higher education landscape. By examining the criteria used, the impact of rankings on universities, and the diverse perspectives of students, we gain a deeper understanding of the complex dynamics shaping the future of higher education.
Understanding the Rankings
The US News & World Report rankings are a highly influential and widely recognized measure of university performance in the United States. These rankings provide a comprehensive overview of various aspects of a university’s academic excellence, research prowess, and overall quality.
Methodology of the Rankings
The US News & World Report rankings are based on a complex methodology that takes into account a wide range of factors, each weighted differently to contribute to the overall score. The methodology is designed to assess universities across various dimensions, including academic reputation, faculty resources, student outcomes, and financial resources.
Factors Considered in the Rankings
The rankings consider several factors to assess a university’s overall performance. These factors can be broadly categorized into:
- Academic Reputation: This factor reflects the perception of a university’s academic excellence within the academic community. It is measured through peer assessments, where faculty members from other institutions are asked to rate the quality of a university’s academic programs.
- Faculty Resources: This factor evaluates the quality and experience of a university’s faculty, including their educational background, research productivity, and teaching experience.
- Student Outcomes: This factor considers a university’s success in graduating students and their subsequent success in the job market. It includes measures such as graduation rates, student retention rates, and the average starting salaries of graduates.
- Financial Resources: This factor examines a university’s financial stability and its ability to support its academic programs and student services. It includes measures such as the endowment size, student-to-faculty ratio, and per-student spending.
Examples of Highly Ranked Universities
Several universities consistently rank high in the US News & World Report rankings. These institutions are recognized for their academic excellence, research achievements, and commitment to student success. Some examples include:
- Princeton University: Princeton University has consistently ranked among the top universities in the US News & World Report rankings, often placing first or second. It is renowned for its rigorous academic programs, distinguished faculty, and world-class research facilities.
- Harvard University: Harvard University is another institution that consistently ranks among the top universities in the US News & World Report rankings. It is recognized for its exceptional academic programs, renowned faculty, and extensive research activities.
- Stanford University: Stanford University is a leading research university with a strong emphasis on innovation and entrepreneurship. It consistently ranks among the top universities in the US News & World Report rankings, known for its academic excellence and research impact.
Global University Landscape
The global landscape of higher education is a complex and dynamic one, with universities across the world competing for recognition and resources. Various ranking systems attempt to capture the multifaceted nature of university excellence, but each has its strengths and weaknesses. This section explores the top universities across different ranking systems, analyzing their strengths and weaknesses, and examining the global distribution of academic excellence.
Comparison of Ranking Systems
Different ranking systems often produce different top 10 lists, reflecting their unique methodologies and criteria. The US News & World Report rankings, for instance, emphasize research output, faculty quality, and student outcomes, while the Times Higher Education World University Rankings consider factors like teaching, research, citations, industry income, and international outlook. The Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU), also known as the Shanghai Ranking, focuses heavily on research performance, measured by the number of Nobel Prize and Fields Medal laureates, highly cited researchers, and publications in prestigious journals.
- US News & World Report: This system is often criticized for its focus on US institutions, with a significant proportion of the top universities being American. Additionally, its methodology relies heavily on subjective data, such as peer assessments, which can be prone to bias.
- Times Higher Education World University Rankings: The Times Higher Education rankings are more globally diverse, including universities from various continents. However, their reliance on citations can favor universities in fields with a higher volume of publications, potentially overlooking institutions with strong teaching and research in less-cited disciplines.
- Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU): The ARWU is known for its emphasis on research output, which can be seen as a narrow measure of university excellence. It may also favor older institutions with a longer history of research achievements, potentially overlooking newer universities with emerging research strengths.
Top Universities by Region
While the US continues to dominate many global university rankings, academic excellence is increasingly evident in other regions of the world.
- Asia: Universities in Asia, particularly in China, South Korea, and Singapore, are rapidly rising in global rankings. These institutions often invest heavily in research infrastructure, attract top international faculty, and prioritize innovation and entrepreneurship. Examples include the National University of Singapore, Tsinghua University, and Peking University.
- Europe: Europe boasts a long tradition of academic excellence, with institutions like the University of Oxford, the University of Cambridge, and Imperial College London consistently ranking among the world’s best. European universities are known for their strong humanities and social sciences programs, as well as their research contributions in fields like medicine, physics, and engineering.
- North America: The US continues to dominate global university rankings, with institutions like Harvard University, Stanford University, and MIT consistently placing in the top 10. These universities are known for their vast research endowments, prestigious faculty, and strong alumni networks. However, the increasing cost of higher education in the US has led to concerns about accessibility and affordability.
- Australia: Australian universities are increasingly recognized for their research excellence and international outlook. Institutions like the University of Melbourne, the University of Sydney, and the Australian National University have established themselves as global leaders in fields like medicine, engineering, and environmental science.
- Latin America: While Latin American universities are generally lower in global rankings, institutions like the Pontifical Catholic University of Chile and the National Autonomous University of Mexico are making significant strides in research and innovation. These universities are actively engaging in collaborations with international partners and developing new research initiatives.
Impact of Rankings on Universities
University rankings, while offering a snapshot of institutional performance, exert a significant influence on various aspects of university life. Their impact extends to admissions, funding, and reputation, shaping the competitive landscape of higher education.
Influence on Admissions
Rankings can significantly influence student choices during the admissions process. Prospective students often prioritize institutions with high rankings, viewing them as indicators of quality and prestige. Universities with top rankings may experience an influx of applications, leading to increased selectivity and a more competitive admissions process. Conversely, institutions with lower rankings may face challenges in attracting top students.
- For instance, a study by the National Center for Education Statistics revealed that the number of applications received by universities ranked in the top 10 increased by an average of 15% over the past decade, while universities ranked outside the top 50 experienced a decrease in applications.
Impact on Funding
Rankings can influence the funding universities receive from various sources. Institutions with high rankings often attract larger endowments, research grants, and private donations. This is because donors and funders often consider rankings as a measure of a university’s success and potential for future impact. Universities with lower rankings may struggle to secure funding, potentially hindering their growth and development.
- For example, a study by the Association of American Universities found that universities ranked in the top 20 received an average of 25% more research funding from the National Institutes of Health than universities ranked outside the top 50.
Reputation and Brand Value
Rankings play a crucial role in shaping a university’s reputation and brand value. Institutions with high rankings are often perceived as prestigious and desirable, attracting top faculty, researchers, and students. This can lead to increased visibility, recognition, and influence in the academic world. Conversely, universities with lower rankings may struggle to attract talent and may face challenges in maintaining their reputation.
- For instance, a university ranked in the top 10 may be more likely to be featured in news articles, attract high-profile speakers, and secure partnerships with leading companies.
Advantages of High Rankings
Being highly ranked offers several advantages for universities. These include:
- Enhanced reputation and prestige, leading to increased visibility and recognition.
- Attracting top students, faculty, and researchers.
- Increased funding opportunities from endowments, research grants, and private donations.
- Improved marketability and competitiveness in the global higher education landscape.
Disadvantages of High Rankings
While high rankings offer benefits, they also present certain disadvantages:
- Pressure to conform to ranking criteria, potentially leading to a narrow focus on metrics at the expense of other important aspects of education.
- Increased competition and a potential emphasis on prestige over substance.
- Potential for ranking manipulation and gaming the system.
Pressure to Conform
Rankings can create pressure on universities to conform to specific standards and metrics used in their calculations. This can lead to a narrow focus on factors that contribute to higher rankings, potentially neglecting other important aspects of education, such as student well-being, diversity, and community engagement.
- For example, some universities may prioritize research output and publications over teaching quality and student support to improve their rankings.
Factors Contributing to University Success
While rankings provide a snapshot of a university’s performance, they don’t tell the whole story. True success extends beyond numerical indicators and encompasses a multifaceted tapestry of factors that drive a university’s impact and influence. This section explores the key elements that contribute to a university’s success, emphasizing the importance of innovation, faculty quality, and student engagement, along with the role of research, entrepreneurship, and community outreach.
The US News & World Report’s annual ranking of top universities is a highly anticipated event, with institutions vying for top spots. Columbia University, consistently ranked among the best, recently held its commencement ceremony, where graduates celebrated their achievements. You can find more information about the ceremony and its highlights on the Columbia University commencement news page.
The university’s continued presence in these prestigious rankings is a testament to its dedication to academic excellence and its commitment to fostering future leaders.
Innovation and Creativity
Innovation is the lifeblood of a thriving university. It fuels groundbreaking research, fosters new technologies, and propels the creation of new knowledge. Universities that prioritize innovation cultivate environments that encourage experimentation, risk-taking, and interdisciplinary collaboration. This can manifest in various forms:
- Establishment of dedicated innovation centers: These centers serve as hubs for research and development, providing resources and support for faculty and students to pursue their innovative ideas. For example, the Stanford University’s d.school, a design thinking program, empowers students to approach challenges with a human-centered design perspective.
- Incentivizing entrepreneurship: Universities can encourage entrepreneurial spirit by providing resources, mentorship, and support for faculty and student startups. The University of California, Berkeley’s Skydeck accelerator program, for example, helps promising startups scale their businesses.
- Fostering a culture of collaboration: By creating environments that encourage interdisciplinary collaboration, universities can foster cross-pollination of ideas, leading to innovative solutions to complex problems. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is renowned for its collaborative research culture, which has resulted in breakthroughs in fields like artificial intelligence and biotechnology.
Faculty Quality and Expertise, Us news and world top universities
A university’s success is intrinsically linked to the quality of its faculty. Exceptional faculty members are not only outstanding educators but also leading researchers and thought leaders who contribute significantly to their fields. A strong faculty:
- Imparts knowledge and inspires students: Highly qualified faculty members are passionate about their subjects and dedicated to student learning. They create engaging learning environments, mentor students, and guide them on their academic journeys.
- Conducts groundbreaking research: Faculty members who are at the forefront of their fields conduct research that advances knowledge, solves real-world problems, and pushes the boundaries of human understanding. For instance, the University of Oxford’s research in vaccine development has had a global impact on public health.
- Engages with the broader community: Faculty members often extend their expertise beyond the classroom, engaging with the community through public lectures, workshops, and consulting projects, sharing their knowledge and contributing to societal progress.
Student Engagement and Success
A university’s success is ultimately measured by the success of its students. Engaged students are more likely to thrive academically, develop essential skills, and make meaningful contributions to society. Universities that prioritize student engagement create environments that:
- Offer diverse learning opportunities: Engaging students in active learning, experiential learning, and research opportunities can foster deeper understanding, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. The University of Michigan’s Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program provides students with the chance to work alongside faculty members on cutting-edge research projects.
- Provide a supportive and inclusive environment: Universities should strive to create a welcoming and inclusive environment that celebrates diversity and supports students from all backgrounds. The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is known for its commitment to diversity and inclusion, fostering a campus where all students feel valued and empowered.
- Connect students with career opportunities: Universities play a vital role in preparing students for successful careers. Providing career counseling, internship opportunities, and alumni networks can help students navigate their career paths and make informed decisions about their future.
Research and Innovation
Research is the cornerstone of a university’s intellectual and societal impact. Through rigorous inquiry and experimentation, universities contribute to the advancement of knowledge, address critical global challenges, and drive innovation. A university’s research prowess is often measured by:
- Research funding and grants: The amount of research funding a university receives is a strong indicator of its research activity and its ability to attract top researchers. For example, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States provides substantial funding for biomedical research at universities across the country.
- Publications and citations: The number of publications and citations a university’s faculty members generate is a measure of their research output and its impact on the field. The University of Cambridge is consistently ranked among the top universities globally for research publications and citations.
- Patents and technology transfer: Universities that are actively involved in research often generate patents and technology transfer agreements, commercializing their research findings and bringing them to market. The University of Texas at Austin has a strong record of technology transfer, with its research leading to the development of innovative technologies in various fields.
Entrepreneurship and Economic Impact
Universities play a crucial role in fostering entrepreneurship and driving economic growth. By supporting startups, incubating new businesses, and fostering innovation, universities contribute to the creation of jobs, economic development, and societal progress. Universities can enhance their entrepreneurial ecosystem by:
- Providing resources and support for startups: Universities can offer mentorship, funding, and access to facilities to help student and faculty entrepreneurs launch their businesses. The University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School has a robust entrepreneurship program that supports aspiring entrepreneurs through workshops, networking events, and funding opportunities.
- Partnering with industry: Universities can collaborate with businesses to conduct joint research, develop new technologies, and create internship and job opportunities for students. For example, the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) has strong partnerships with local companies in the biotech and technology sectors.
- Creating innovation hubs: Universities can establish innovation hubs or technology parks to foster entrepreneurship and attract businesses. The University of Oxford’s Science Park is a prime example of a successful innovation hub, home to numerous startups and research companies.
Community Outreach and Engagement
A successful university is not an isolated entity but an active participant in its surrounding community. Through community outreach and engagement, universities can share their expertise, contribute to societal progress, and build strong relationships with their stakeholders. Examples of community engagement include:
- Public lectures and workshops: Universities can offer public lectures and workshops to share their knowledge with the community on topics of current interest. The University of Chicago’s Harris School of Public Policy regularly hosts public events on issues related to public policy and governance.
- Community service projects: Universities can encourage students and faculty to participate in community service projects, addressing local needs and building connections with the community. The University of Washington’s Volunteer Center connects students with various community service organizations.
- Partnerships with local organizations: Universities can partner with local organizations to conduct research, provide training, and support community initiatives. The University of Maryland, College Park, has a strong partnership with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), collaborating on research and development projects.
Student Perspectives on University Rankings: Us News And World Top Universities

University rankings are a significant factor for many students during the college application process. While they provide a general overview of institutions’ academic reputation and performance, students also consider other factors beyond rankings when making their decision.
Factors Beyond Rankings
Students prioritize various factors beyond rankings, recognizing that a university’s position on a list doesn’t necessarily guarantee a fulfilling educational experience. These factors include:
- Program Quality: Students often prioritize the quality and reputation of specific programs, particularly in their chosen field of study. They research faculty expertise, curriculum, and program outcomes to ensure a strong academic foundation.
- Campus Culture: Students seek a campus environment that aligns with their values and interests. They consider factors like student diversity, extracurricular activities, and the overall social atmosphere to find a place where they can thrive.
- Career Prospects: Students are increasingly concerned about their future career paths. They research universities’ career services, alumni networks, and industry connections to assess their potential for job placement and career advancement.
- Cost and Financial Aid: The cost of attending a university is a significant factor for many students. They consider tuition fees, living expenses, and financial aid opportunities to determine affordability.
- Location and Accessibility: Location plays a crucial role in student decisions. They consider factors like proximity to home, urban or rural setting, and access to transportation and amenities.
Examples of Students Choosing Based on Factors Other Than Rankings
Many students have chosen universities based on factors beyond rankings. For instance, a student passionate about environmental studies might choose a university known for its strong sustainability programs, even if it doesn’t rank among the top institutions overall. Similarly, a student aspiring to become a musician might prioritize a university with a renowned music program, regardless of its ranking.
The Role of Universities in Society
Universities are not just institutions of higher learning; they are vital pillars of society, contributing significantly to education, research, and economic development. They act as engines of innovation, fostering critical thinking, and shaping the future of our world.
Impact on Education
Universities play a central role in shaping the future of society by educating the next generation of leaders, innovators, and citizens. They provide access to knowledge, skills, and values that are essential for success in the 21st century. The knowledge and skills gained within university walls equip individuals to contribute meaningfully to their communities and the world. Universities offer a diverse range of academic programs, fostering intellectual curiosity and promoting lifelong learning.
Role in Research and Innovation
Universities are at the forefront of scientific discovery and technological advancement. They serve as hubs for research and innovation, generating new knowledge and solutions to pressing global challenges. Research conducted in universities contributes to advancements in medicine, engineering, technology, and other fields. These advancements have the potential to improve lives, create new industries, and drive economic growth.
Economic Development
Universities are economic engines, driving growth and prosperity in their surrounding communities. They attract talented individuals, create jobs, and stimulate innovation. The knowledge and skills developed within universities contribute to the creation of new businesses and industries, fostering economic diversification and competitiveness. Universities also contribute to economic development through partnerships with local businesses and government agencies.
Relationship with Local Communities
Universities have a deep and enduring relationship with their local communities. They serve as cultural centers, offering museums, art galleries, theaters, and other public spaces. They also engage in community outreach programs, providing educational opportunities, healthcare services, and social support. Universities contribute to the cultural and social fabric of their communities, promoting diversity, inclusion, and civic engagement.
Challenges and Opportunities
Universities face a number of challenges in the 21st century, including increasing costs, pressure to be more accountable, and the need to adapt to changing technological landscapes. However, they also have significant opportunities to make a positive impact on society. Universities can play a key role in addressing global challenges such as climate change, inequality, and poverty. They can also leverage their expertise and resources to promote peace, justice, and sustainable development.
Diversity and Inclusion in Top Universities
The pursuit of academic excellence should be inclusive and welcoming to all, regardless of background. Top universities, often seen as bastions of intellectual pursuit, have a responsibility to reflect the diverse world they inhabit. This section examines the representation of diverse populations within these institutions, the efforts being made to promote diversity and inclusion, and strategies for increasing access for underrepresented groups.
Representation of Diverse Populations
Examining the demographics of top-ranked universities reveals both progress and persistent challenges. While some institutions have made strides in increasing the representation of historically underrepresented groups, others continue to lag behind. A comprehensive analysis of student bodies across various universities is crucial to understand the current landscape and identify areas for improvement.
- Racial and Ethnic Diversity: While progress has been made in recent years, the representation of racial and ethnic minorities in top universities remains uneven. For example, the percentage of Black and Hispanic students at elite institutions often falls significantly below their proportion in the general population. This disparity reflects systemic barriers and a lack of equal access to opportunities.
- Socioeconomic Diversity: Access to top universities is often tied to socioeconomic background. Students from low-income families are significantly underrepresented, highlighting the need for greater financial aid and support programs. This lack of representation limits the diversity of perspectives and experiences within these institutions.
- Gender Diversity: While women have made significant gains in higher education, their representation in STEM fields and leadership positions within top universities remains a concern. Addressing gender bias and promoting equal opportunities are crucial for creating a more balanced and equitable academic environment.
- International Diversity: Top universities increasingly attract students from around the globe, contributing to a vibrant and diverse learning environment. However, ensuring equitable access for international students and fostering a welcoming atmosphere for them is crucial.
Efforts to Promote Diversity and Inclusion
Recognizing the importance of diversity and inclusion, many top universities have implemented initiatives to create more welcoming and equitable environments. These efforts encompass a range of approaches, from recruitment and admissions practices to faculty development and campus culture.
- Targeted Recruitment and Outreach: Universities are actively engaging in targeted recruitment efforts to reach underrepresented groups. This includes partnerships with community organizations, outreach programs, and targeted advertising campaigns to broaden the pool of potential applicants.
- Financial Aid and Scholarships: Increased financial aid and scholarships are crucial for making top universities accessible to students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. This includes need-based aid, merit-based scholarships, and programs designed to support first-generation college students.
- Diversity and Inclusion Training: Many universities provide training programs for faculty, staff, and students to promote awareness of diversity and inclusion issues. This training aims to foster understanding, empathy, and a commitment to creating an inclusive environment.
- Campus Culture and Climate: Creating a welcoming and inclusive campus culture is essential. This includes fostering a sense of belonging for all students, addressing microaggressions, and promoting dialogue and understanding across diverse perspectives.
Strategies for Increasing Access for Underrepresented Groups
While progress has been made, more can be done to increase access to top universities for underrepresented groups. A comprehensive approach is needed, involving partnerships with K-12 schools, increased financial aid, and systemic changes within higher education.
- Early Intervention and Support: Initiatives aimed at supporting underrepresented students from an early age are crucial. This includes mentorship programs, STEM outreach programs, and college readiness workshops to encourage academic success and prepare students for higher education.
- Holistic Admissions Processes: Universities should move beyond standardized test scores and consider a more holistic admissions process that takes into account a student’s overall potential, extracurricular activities, and life experiences. This approach can help identify talented students from diverse backgrounds who may not have had access to the same opportunities.
- Addressing Systemic Barriers: Systemic barriers, such as implicit bias and institutional practices that perpetuate inequality, must be addressed. This includes reviewing admissions criteria, faculty hiring practices, and campus policies to ensure fairness and equity for all.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between universities, government agencies, and private organizations is essential to create a more equitable system of higher education. This includes funding initiatives, supporting outreach programs, and advocating for policy changes that promote access and opportunity for all.
Future Trends in Higher Education
The landscape of higher education is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving student expectations, and the changing needs of the global economy. Emerging trends like online learning, personalized education, and interdisciplinary research are reshaping how universities operate and how students learn. These trends have the potential to significantly impact university rankings, and universities that adapt to these changes will be well-positioned to thrive in the future.
The Rise of Online Learning
The growth of online learning platforms and massive open online courses (MOOCs) has made education more accessible and flexible. Online learning offers several advantages, including:
- Accessibility: Online learning removes geographical barriers, allowing students from around the world to access high-quality education.
- Flexibility: Online courses offer greater flexibility in terms of learning pace and schedule, accommodating the needs of working professionals and students with diverse commitments.
- Cost-effectiveness: Online courses can be significantly cheaper than traditional on-campus programs, making education more affordable for a wider range of students.
The increasing popularity of online learning has led to a rise in blended learning models, where online and in-person instruction are combined. This approach offers students the best of both worlds, allowing them to benefit from the flexibility of online learning while still experiencing the social and collaborative aspects of traditional education.
Personalized Education
The rise of personalized learning is driven by the recognition that students learn at different paces and have different learning styles. Personalized education involves tailoring educational experiences to meet the individual needs of each student. This can involve:
- Adaptive learning platforms: These platforms adjust the difficulty and pace of learning materials based on the student’s progress and understanding.
- Personalized learning pathways: Students can choose from a variety of learning pathways that align with their interests and career goals.
- Personalized feedback and support: Students receive tailored feedback and support from instructors and mentors, helping them to identify areas for improvement and stay on track.
Personalized education can lead to more engaging and effective learning experiences, but it also requires significant investment in technology and faculty development. Universities that embrace personalized learning will need to adapt their infrastructure and teaching practices to meet the demands of this new approach.
Interdisciplinary Research
The traditional boundaries between academic disciplines are becoming increasingly blurred as new challenges and opportunities emerge. Interdisciplinary research, which combines perspectives and methodologies from multiple disciplines, is essential for tackling complex problems such as climate change, artificial intelligence, and global health.
- Collaboration across disciplines: Interdisciplinary research requires collaboration between researchers from different fields, fostering a culture of cross-disciplinary dialogue and innovation.
- Addressing complex challenges: Interdisciplinary research is essential for tackling complex problems that cannot be solved by a single discipline alone.
- Developing new solutions: By combining perspectives from different fields, interdisciplinary research can lead to the development of innovative solutions that address real-world problems.
Universities that encourage and support interdisciplinary research will be well-positioned to attract top researchers and make significant contributions to knowledge creation and societal progress.
Impact on University Rankings
The rise of online learning, personalized education, and interdisciplinary research will have a significant impact on university rankings. Traditional ranking systems often prioritize factors such as research output, faculty credentials, and student selectivity. However, these factors may not fully capture the value of these emerging trends.
- Innovation in teaching and learning: Universities that embrace innovative teaching and learning approaches, such as online learning and personalized education, will be recognized for their commitment to student success and adaptability.
- Impact of research: Universities that prioritize interdisciplinary research and focus on addressing real-world challenges will be recognized for their contribution to societal progress and global impact.
- Accessibility and affordability: Universities that make education more accessible and affordable through online learning and innovative financing models will be recognized for their commitment to social equity and inclusion.
Universities that adapt to these trends will need to develop new metrics and indicators that reflect the value of these innovations. This will require a shift in how universities are evaluated and ranked, moving beyond traditional measures and embracing a more holistic approach that considers the impact of education on society and the world.
Predictions for the Future
The future of top universities is likely to be shaped by the ongoing evolution of these trends. Universities that embrace these trends will be well-positioned to attract top students and faculty, drive innovation, and make a positive impact on the world.
- Increased focus on online learning: Online learning will continue to grow in popularity, and universities will need to invest in developing high-quality online programs and platforms.
- Personalized learning as the norm: Personalized education will become increasingly prevalent, and universities will need to adapt their teaching practices and infrastructure to support this approach.
- Interdisciplinary research as a key driver of innovation: Interdisciplinary research will play an increasingly important role in tackling global challenges and driving innovation.
- New ranking systems: New ranking systems will emerge that prioritize factors such as innovation in teaching and learning, impact of research, and accessibility and affordability.
The future of top universities will be characterized by a commitment to innovation, adaptability, and social responsibility. Universities that embrace these trends will play a critical role in shaping the global landscape of higher education and preparing students for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
Data Visualization of University Rankings
Data visualization plays a crucial role in understanding and interpreting complex data, especially when it comes to university rankings. Visual representations can effectively convey trends, patterns, and comparisons, providing insights that might be missed when examining raw data alone. By using different visualization techniques, such as tables, charts, and maps, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the university landscape and the factors that contribute to their success.
Top 10 Universities in the US News & World Report Rankings
This table presents the top 10 universities in the US News & World Report rankings, highlighting their overall rank, location, and key strengths.
| Rank | University | Location | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Princeton University | Princeton, New Jersey | Academics, Faculty, Research |
| 2 | Harvard University | Cambridge, Massachusetts | Academics, Faculty, Research, Global Impact |
| 3 | Columbia University | New York, New York | Academics, Faculty, Research, Location |
| 4 | Stanford University | Stanford, California | Academics, Faculty, Research, Innovation |
| 5 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | Cambridge, Massachusetts | Academics, Faculty, Research, Innovation |
| 6 | Yale University | New Haven, Connecticut | Academics, Faculty, Research, Global Impact |
| 7 | University of Pennsylvania | Philadelphia, Pennsylvania | Academics, Faculty, Research, Location |
| 8 | University of Chicago | Chicago, Illinois | Academics, Faculty, Research, Innovation |
| 9 | Duke University | Durham, North Carolina | Academics, Faculty, Research, Student Life |
| 10 | California Institute of Technology (Caltech) | Pasadena, California | Academics, Faculty, Research, Innovation |
Comparison of University Rankings Across Factors
This bar chart visually compares the rankings of different universities across various factors, such as academic reputation, research activity, and student outcomes. The height of each bar represents the university’s ranking in that specific factor.
For example, a university with a high bar for academic reputation would be considered highly regarded in the academic community.
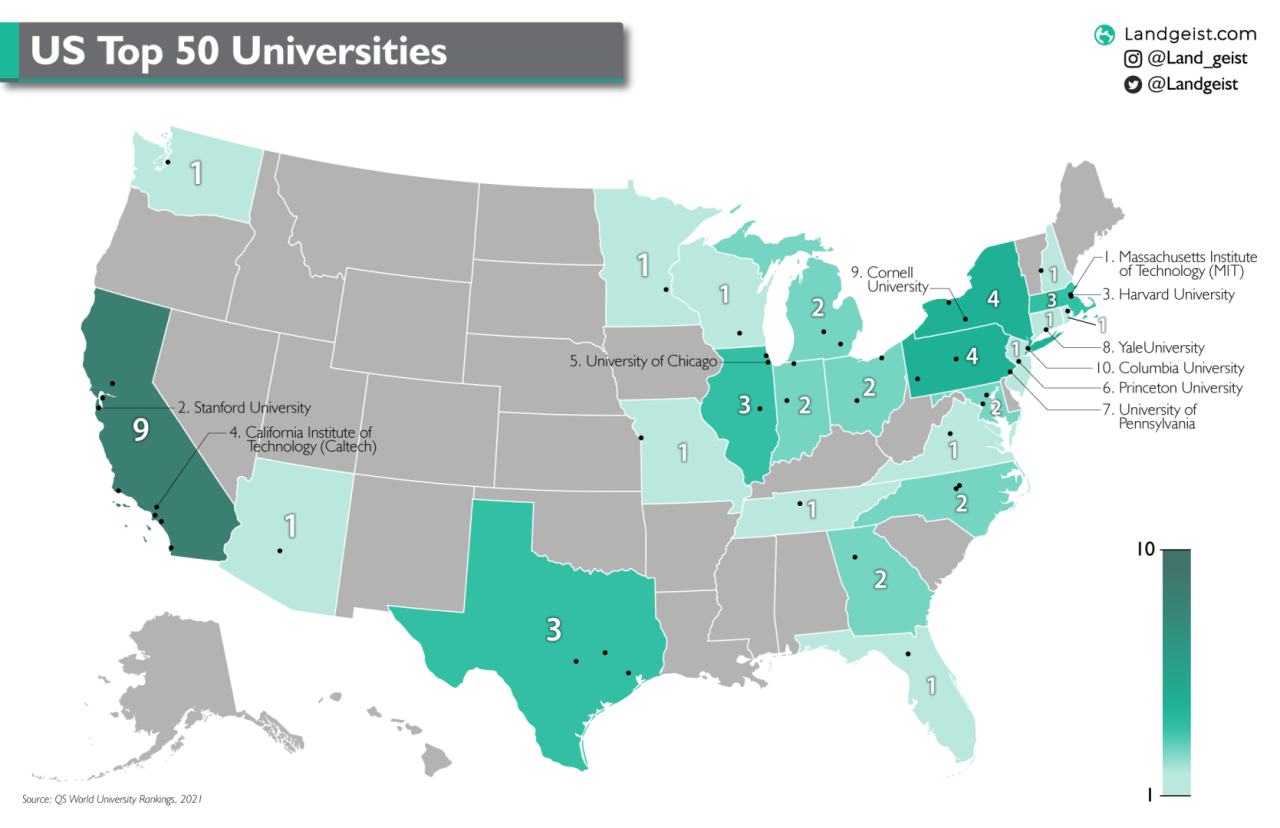
Geographical Distribution of Top Universities
This map shows the geographical distribution of the top universities in the US News & World Report rankings. The size of each marker represents the university’s overall rank.
This visualization helps identify clusters of top universities and provides insights into the geographical concentration of higher education excellence.
As we conclude our exploration of US News & World Report Top Universities, it becomes evident that these rankings offer a valuable, albeit nuanced, lens through which to view the world of higher education. While acknowledging the potential limitations of rankings, we recognize their significant influence on university admissions, funding, and global perception. Ultimately, the true measure of a university’s success lies not solely in its ranking but in its commitment to academic excellence, innovation, and societal impact.
The US News & World Report’s annual rankings of top universities are eagerly awaited by prospective students and their families. Boston University, a highly regarded institution, consistently features prominently on these lists. To stay up-to-date on the latest news and developments at Boston University, check out their official news website, boston university news. The rankings, while valuable, are just one factor to consider when making such an important decision about your future.